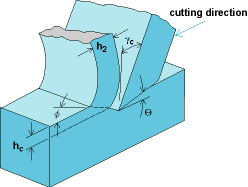
Feed (f) : Distance between newly machined surface and the chip evolved is called.
Clearance Angle : The angle we provide between the flank face of tool and newly machined surface so that no rubbing can take place between tool and machined surface. It is alwayes provided to the cutting tool to provide loss of energy and damages to both work piece and the tool. typical range of clearance angle is from 3 degrees to 5 degrees, depending upon tool work piece material and the type of machining operation like turning , boring , milling etc...
Rake angle : The angle formed between the rake face of the tool and cutted chip.
+ve rake angle : Positive rake angle helps reduces the cutting forces.
-ve rake angle : To increase edge strength and the life of the tool.
zero rake angle : To simplify the design of the tool.
Tool chip contact length : The point from where chip started and ditached the tool's rake face is called tool-chip contact length.
Advance Manufacturing | Manufacturing Processes
Monday, November 29, 2010
Thursday, November 25, 2010
Orthogonal and Oblique Cutting
Orthogonal Cutting: The cutting condition when chip is expected to flow along the orthogonal plane is known as orthogonal cutting.pure orthogonal cutting is orthogonal cutting when principle cutting angle is 90 degree.
Oblique Cutting: When the chip does not flow on orthogonal plane i.e chip deviates from orthogonal plane then it is called oblique cutting.
Basic Difference Between Orthogonal and Oblique Cutting: in oblique cutting inclination angle(lamda) have some value but in orthogonal cutting there is no lamda i.e lamda=zero.
Causes of orthogonal cutting:
Oblique Cutting: When the chip does not flow on orthogonal plane i.e chip deviates from orthogonal plane then it is called oblique cutting.
Basic Difference Between Orthogonal and Oblique Cutting: in oblique cutting inclination angle(lamda) have some value but in orthogonal cutting there is no lamda i.e lamda=zero.
Causes of orthogonal cutting:
- Restricted cutting effect.
- tool nose radius-ing.
- inclination angle (Lamda not equal to zero).
Cutting Tools
In the context of machining, a Cutting Tool (or a Cutter) is a tool used to remove material from work piece by means of shear deformation.
Types of cutting tools:
(according to feature)
There are two types of cutting tools,
- Single Point Cutting Tool.
- Multiple Point Cutting Tool.
Multiple Point Cutting Tools: Multiple Point Cutting Tools are often used in milling and drilling. Grinding tools are also multiple point cutting tools.
Note:
- Cutting Tool must be made of harder material than the work piece material(which is to be cut).
- The Tool must withstand the heat generated during cutting operations.
- Tool must have specific geometry with clearance angles so that the cutting edge of the tool can contact the work piece with out the rest of the tool dragging onto the surface of the work piece.
- The angle of the cutting face is also important.
Important Terminologies
Chips: The removed part of work piece while performing machining. Usually in a curved layer form which ejects out.
Machining: The process of removing unwanted material from work piece in the form of chips.
Metal Cutting: machining can be referred to as Metal Cutting when work piece is Metallic.
The term machining is further divided in to following sections.
Drilling:
Turning:
Milling:
Grinding:
Machining: The process of removing unwanted material from work piece in the form of chips.
Metal Cutting: machining can be referred to as Metal Cutting when work piece is Metallic.
The term machining is further divided in to following sections.
Drilling:
Turning:
Milling:
Grinding:
Difference between SHAPER and PLANNER
In Shaper machine, tool is having reciprocating motion and w/p is clamped on table which is stationary. It is mostly suitable for light duty operation.In Shaping large cutting force is transferred to tool. In Planer machine, tool is having stationary and w/p is clamped on table which is reciprocating moton. It is mostly suitable for Heavy duty operation.In planner large cutting force is transferred to table.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)